The application settings dialog controls the behavior of qdmr. The dialog is divided into 3 sections, accessible via the tabs on the top.
The Data Sources tab collects the settings for the location service and repeater database.
 |
[D]
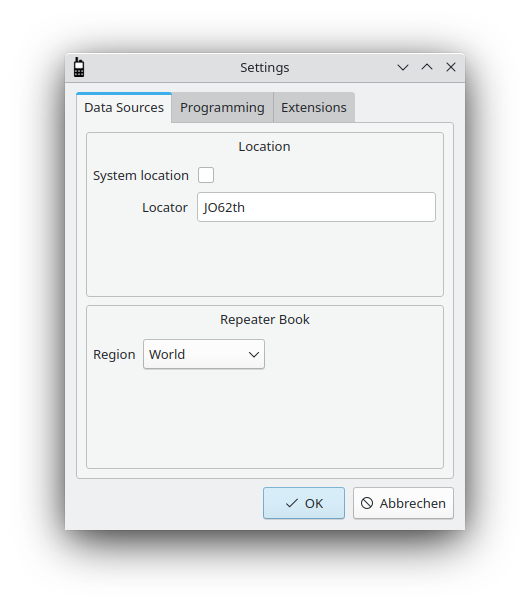
The settings dialog: Data sources
The first section concerns the location of the user. You may enter your Maidenhead Locator here or you may enable System location. The latter tries to obtain the current location from the operating system. This information is then used in the channel editors (see the section called “Creating Channels”) to provide auto-completion for repeaters nearby.
The second section allows to set the source for the repeater database. This enables qdmr to automatically complete some information for a repeater if its callsign is entered as the name, when creating a new channel. For some weird reason, the single data source Repeater Book provides two identical APIs for North America and the rest of the World. You must select your source accordingly.
The second tab controls, how the radios are programmed. That is, how the codeplug is assembled and also, how the callsign database gets curated.
 |
[D]
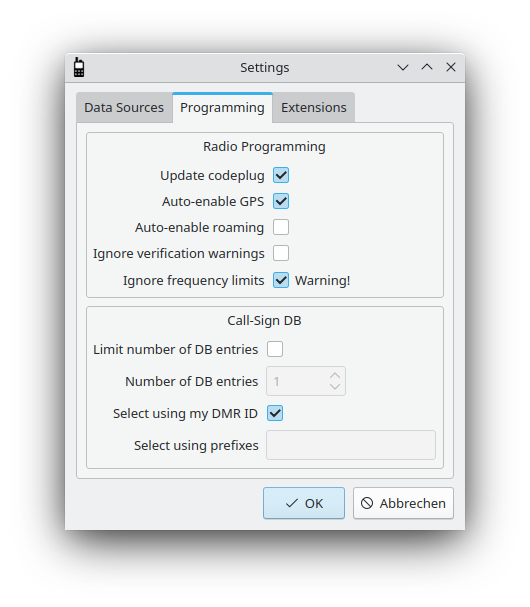
The settings dialog: Programming
The Radio Interfaces section contains settings, controlling, how the radios are accessed. For now, there is only one setting, called disable auto-detect. This will disable all means to detect and identify connected radios. You will then have to select an interface and choose a radio model, every time you access it.
The second section specifies how codeplugs are assembled. The first option Update codeplug specifies whether a codeplug is generated from scratch or whether the codeplug currently programmed on the radio gets updated. qdmr does not implement all settings possible for all radios, consequently Update code plug should be chooses to maintain all settings of the radio that are not touched by qdmr.
For some radios, the GPS and roaming functionality must be enabled explicitly. The Auto-enable GPS and Auto-enable roaming options can be used to automatically enable GPS or roaming. If selected, whenever any channel has a GPS/APRS system or a roaming zone associated with it, the GPS and/or roaming gets enabled globally.
As described in the section called “Programming the radio”, the upload of a code plug will be paused if some verification warnings are issued. The Ignore verification warnings option allows to continue silently even in the presence of verification warnings. The may be needed for some radios with some rather short communication timeout. The radio may reset the connection to the computer while the warnings are shown. To prevent this, this option might be used.
The Ignore frequency limits option does exactly what it says. Usually, programming a channel outside of the radios frequency range would issue an error. However, many radios are able to receive and even transmit outside of the frequency range specified by the manufacturer. But be aware, that transmitting outside the declared frequency range may destroy the radio!
The Call-Sign DB section collects options that control the automatic curation of the call-sign DB. Many radios allow to write a large database of call-signs and DMR IDs to the radio. These DBs are then used to resolve DMR IDs to call-signs, names etc. and display them.
Usually, curating these databases is a cumbersome task. qdmr tries to automate this task. Usually, qdmr will select as many call-signs from the global database it can fit into the radio. Although modern radios will provide a huge amount memory, not all registered IDs can be programmed. In these cases, qdmr will select only the closest IDs to your DMR ID (default Radio DMR ID, see the section called “General configuration”). The DMR IDs are compared by the longest matching prefix. This makes sense as DMR IDs are not random. They share the same prefix for countries and regions. This way, qdmr will first select all IDs from the same region followed by all IDs from the same country etc. Of cause, there is no rule without any exceptions. Some countries have several prefixes assigned.
The Limit number of DB entries option and Number of DB entries field allow to limit the number of DB entries written to the device. If the Limit number of DB entries option is disabled, as many entries are written to the device as it can hold.
The Select using my DMR ID option and the Select using
prefixes field can be used to control the selection of entries. If the
Select using my DMR ID option is enabled, the aforementioned algorithm is
used to select the entries based on the default DMR ID. If this option is disabled, a list of
prefixes must be specified in
the Select using prefixes field. This must be a list of comma-separated
prefixes like 262, 263. Whitespace are ignored. Then the DMR IDs closest to these
prefixes are used to assemble the final call-sign DB.
The last tab collects settings, controlling several extended settings for the devices.
 |
[D]
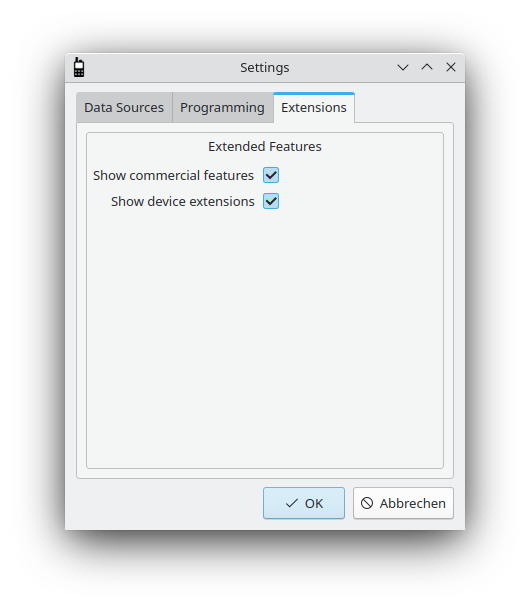
The settings dialog: Extensions
DMR originated as a standard for commercial radios. Consequently, there are many features that are not relevant or even illegal for ham-radio use (e.g., encryption). However, some operators use their handhelds for both ham-radio and commercial applications. Consequently, qdmr cannot ignore commercial features. It can, however, hide them. Enabling the Show commercial features options will show these features.
Starting with qdmr version 0.9.0, there are some device specific settings, allowing to configure features only present in one device and not represented in the general code plug. These are called extensions and are usually hidden. To show these device specific extension, select Show device extensions.