Roaming is a feature that allows DMR radios to select an alternative repeater once you leave the range of the currently selected one. To do that, you have to specify so-called roaming zones. Within these zones, you collect all repeaters that provide access to a particular talk group. When roaming is enabled, the radio will check periodically, whether the current repeater is still reachable. If not, the strongest repeater from the selected roaming zone will then be selected instead.
In order to stay connected to a particular talk group, not the entire channel settings must be changed. But only those properties, that are specific to the repeater we change to. These are the RX and TX frequencies, color codes and sometimes the time-slot. The latter is necessary, as those repeaters may be located in other regions. Usually — at least for Brandmeister repeaters — the time slot 2 is reserved for regional communication while time slot 1 is intended for inter-regional communication. So you may need to override the time-slot of the active channel, whenever you roam outside of the region associated with the talk group. Some talk groups, however, are over-regional anyway. For example, the world-wide talk group 91. Here, the time slot will always be TS 1 and thus does not need to be overridden.
As only some properties of the current DMR channel needs to be overridden, there are special channels called roaming channels that contain only those settings, that are changed during roaming.
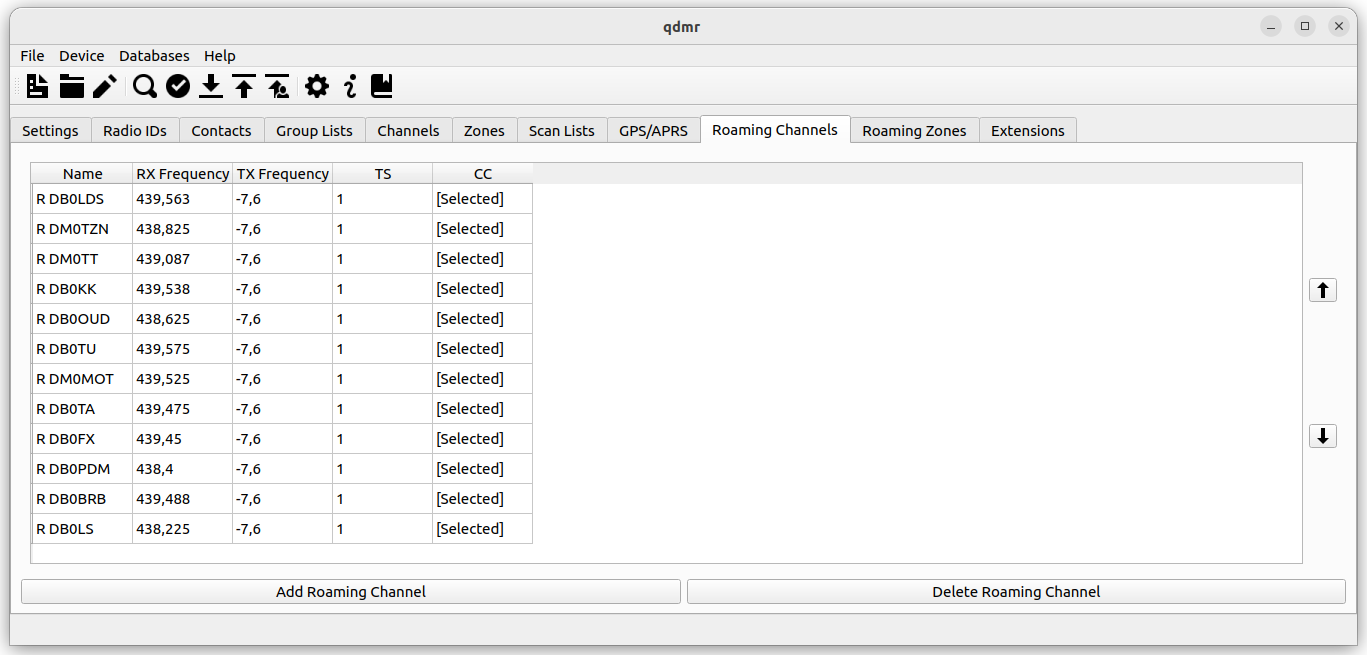
The Roaming Channels tab collects all defined roaming channels.
 |
[D]
List of roaming channels.
Each roaming channel has a name, for easy reference in the roaming zones. This should be the call of the repeater. Additionally, each roaming channel has a transmit (TX) and receive (RX) frequency overriding the TX and RX frequencies of the current channel on roaming.
There are two optional settings, that may override the time slot (TS) and color code (CC) of the current channel. If [Selected] is show, the time slot and color code of the current channel is used instead during roaming.
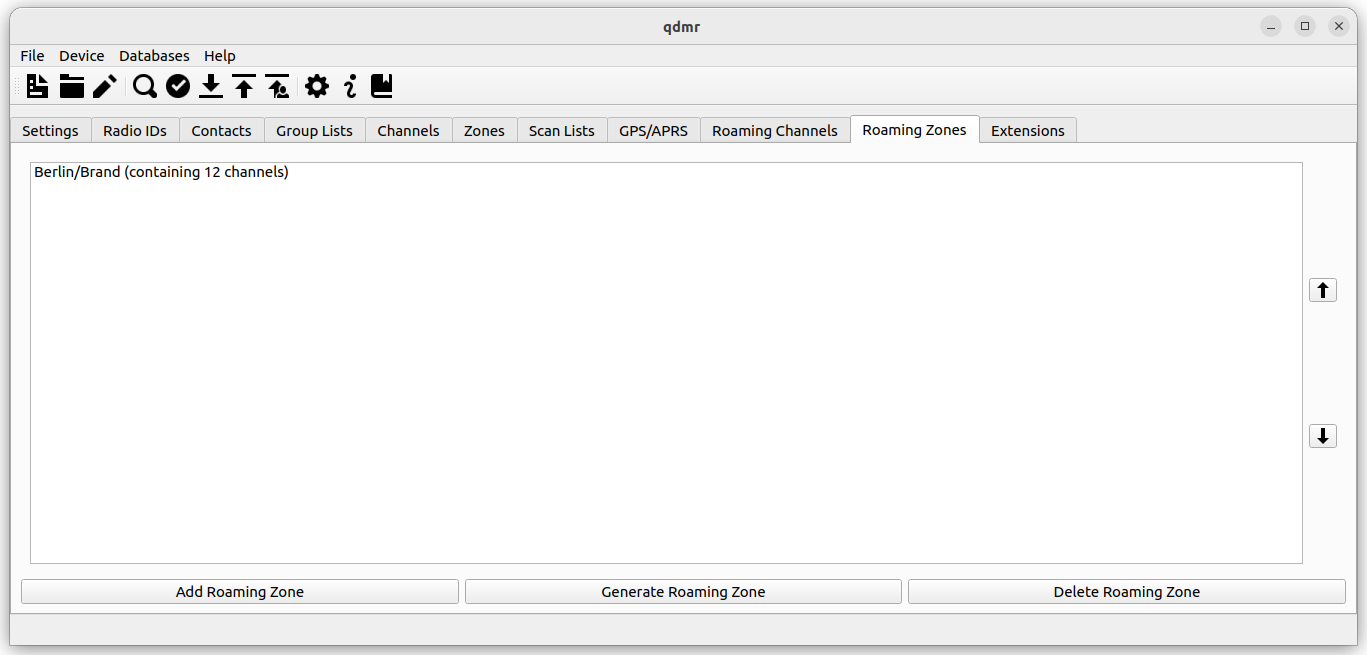
The Roaming Zones tab collects all defined roaming zones.
 |
[D]
List of roaming zones.
There are two ways to create a new roaming zone. The easiest way is to generate a zone and the associated roaming channels automatically. Click on , to generate a roaming zone automatically or to assemble one manually.
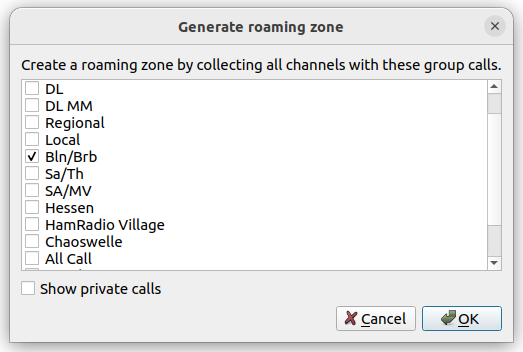
When generating a roaming zone automatically, a dialog will you to select a talk group or several talk groups to create a roaming zone for. That is, the talk group you want to stay connected to in case of losing contact to the repeater.
 |
[D]
Selecting talk groups to generate a roaming zone.
Once a talk group is selected, a roaming channel created for each DMR channel, which has the selected talk group as its transmit contact. These newly created channels are then collected into a new roaming zone. The roaming zone editing dialog is then opened, allowing you to edit the newly created zone.
Alternatively, you may create a roaming zone manually. Simply click the button and the roaming zone editing dialog will open. There you can add roaming channels manually.
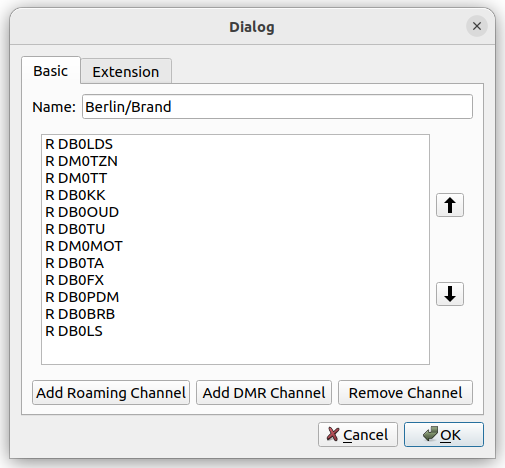
Double-clicking on the roaming zone or clicking on the button will open the Roaming Zone Editor.
 |
[D]
The roaming-zone editing dialog.
Here you can edit the name of the roaming zone as well as adding the roaming channels that are part of this zone. However, you may also add DMR channels to this zone by clicking on the button. This will not add DMR channel directly to the roaming zone, but will create a new roaming channel from this DMR channel.
If Show Commercial Features is enabled in the settings dialog (see the section called “Application Settings Dialog”), a tab bar is shown at the top. There you can also access the device specific settings for the roaming zone.